About McStas
Conditions of use
Authors/Contacts
Project funding
Download
Components
Other Downloads (share)
Documentation
Wiki (GitHub)
McStas manual
Publications
December 20th, 2020: Experimental Docker image with McStas 3.0 and NVIDIA HPC SDK
Dear all,
Fitting McStas and the NVIDIA HPC SDK in a live-dvd has proven very challenging.
Instead, an experimental docker solution has been made available at https://github.com/mccode-dev/McCode/tree/mcstas-3.0/Docker/mcstas/3.0-fat-with-nvhpc
Minimal usage instructions are available at https://github.com/mccode-dev/McCode/blob/mcstas-3.0/Docker/README.md
More detailed instructions will arrive in 2021.
December 17th, 2020: Ubuntu 20.4 live-dvd with 2.7 and 3.0 releases.
Dear all,
At http://livedvds.mcstas.org a Ubuntu 20.04 live system, pre-loaded with McStas 2.7 and 3.0 has been uploaded.
Here are some tips:
- The live-system user is "mcstas" with password "mcstas".
- You may use it to try either release, either from the live image or by choosing the "install" option at the boot-loader.
- Both of the new McStas relases have been installed, the system default is McStas 3.0.
- If you run this command:
cp /etc/skel/Desktop/McStas* Desktop
two desktop-launchers for the two versions will appear on your desktop. - You may change the system-default McStas to 2.7 by running the
following commands in a terminal:
sudo -i mcstas-2.7-environment postinst set_mccode_default
An alternative version including McStas 3.0 only, and loaded with the NVIDIA HPC-SDK is in preparation.
December 15th, 2020: McStas 3.0 release!
Dear all,
McStas, v. 3.0, our next-generation code generator and support for NVIDIA GPU's via OpenACC has been built and is ready for download!
Download and installation instructions are available via our GitHub download pages.
Selected highligts from the release are listed below. The full list of changes is also available at http://mcstas.org/CHANGES_McStas.
Thanks:
Main new features and changes:
- New code-generation scheme based on functions instead of #defines, which brings
- Much improved compilation-times, the code is better suited for modern compilers
- In most cases a speed-up of order 20%
- The neutron _particle is now represented by a struct
- The component types and instances are also represented by structs
- In the generic TRACE function of a given component type, the _comp var is short-hand for "whatever the component instance is"
- New instrument section of USERVARS %{ double example_flag; %} which enriches the _particle struct
- In component DECLARE blocks, assignments can no longer be done and all declarations must be listed independently, i.e double a; is OK, double a,b; is not. Variables in this scope are automatically so-called "OUTPUT PARAMETERS" (we may deprecate that keyword completely for the official McStas 3.0 release)
- Components no longer support DEFINITION PARAMETERS, instead the SETTING PARAMETERS must be used, which now includes a vector and string type supplementing the (default) double/MCNUM and int types.
- Further, the new cogen implements support for Nvidia GPU's, for details see point 2 below.
- Support for OpenACC acceleration on NVIDIA GPU's on Linux systems
- #pragma driven, inserted by the code-generation, but also implemented in libs and comps
- Speedups measured using top-notch NVIDIA V100 datacenter cards are in the range of 10-600 with respect to a single-core of a modern CPU, see the figure in the below link. It was generated for an "ideally" parallel instrument.
- Platform support / compiler configuration:
- Required compiler for GPU/OpenACC: NVIDIA HPC SDK 20.x or newer. Community edition works fine
- Required GPU hardware: NVIDIA Tesla card + configured driver
- Windows: At this point UNSUPPORTED for GPU/OpenACC since NVIDIA does not yet ship a package for this platform. Support should come with WSL 2.0 or via native support from NVIDIA.
- macOS: At this point UNSUPPORTED for OpenACC since NVIDIA does not ship a package for this platform.
- Linux: Full acceleration support with GPU, and with CPU/multicore.
- Install the compiler and put it on your system PATH. Install and configure Nvidia drivers for your card.
- We hope that GCC will offer better support for OpenACC in the near future.
- Tool support
- On Linux and macOS mcrun is preconfigured so that mcrun -c --openacc compiles with:
- Linux: nvc -ta:tesla,managed,deepcopy -DOPENACC
- Linux: You may configure for use on CPU/multicore via: nvc -ta:multicore -DOPENACC
- The --funnel option can be used to launch the FUNNEL simulation flow, see description below.
- For both of the above, adding -Minfo:accel will output verbose information on parallelisation
- In mcgui, the mcrun --openacc configuration can be selected via the preferences
- Both mcgui and mcrun allow combining --openacc and --mpi if you have multiple GPU's available. The n'th mpi process will attempt to use the k'th GPU, where k = #available GPU's % #MPI nodes.
- Special McStas 3.0 grammar for mixed CPU/GPU mode:
- A "FUNNEL" mode has been added, which allows
- Mixed GPU/CPU mode, were sections of the instrument are executed on each device type, with copying of neutron-bunches back and forth.
- When this instrument grammar is specified, it signifies that the component should be executed on CPU rather than GPU. CPU SPLIT 10 COMPONENT Sample = Something()
- Sections before and after that are not marked CPU will be executed on GPU.
- If a component includes the NOACC token in the component header, the CPU-mode is forced through the compilation, as it signifies that the component does NOT support GPU. This is for the time being the case for Union_master. (Support is expected to come with McStas 3.1)
- A "FUNNEL" mode has been added, which allows
- Interoperability with McStas 2.7
- Support for MCPL event interchange has been added through MCPL_input and MCPL_output components, that work both on CPU and GPU for McStas 3.0. Note however that targeting GPU, MCPL_input reads ALL particle events durin INITIALIZE and MCPL_output writes ALL particle events during SAVE, whereas when using CPU in 3.0 or 2.7, reads and writes happen during the TRACE flow.
- Known limitations
- The Union subsystem works on CPU only for now, but can be used in the mixed GPU/CPU funnnel mode as mentioned above. Union_master is a NOACC component.
- The same solution is applied in use of the NCrystal_sample and will eventually come for Sample_nxs.
- Not all features of all components correspond to those from McStas 2.7, but all essential components have beenfully ported from the 2.7 tree to the 3.0 tree. Hence, some parts distributed with McStas 2.7 will either not exist in the 3.0 release or may not function, due to either: (1) very specialised features (2) maintainability issues or (3) use ofcomplex algorithms.
- Generally, most components/instruments are now ported to our OpenACC based GPU-technology, but you
likely may find combinations of use that slipped through our not fully exhaustive test-suite. Missing
support may come in the form of either
- Code that does not compile
- Instruments that segfaults during execution
- Instruments or components that produce obscure results
- At the time of release, the nightly tests
show that
- McStas 3.0 ships with 211 instruments that succesfully compiles
- These instruments use 147 of our components
- We don't ship an updated set of manuals for McStas 3.0, but essential documentation is available on the McCode GitHub wiki



December 12th, 2020: Scheduled downtime for McStas webserver on December 14th
The McStas webserver will be down during Monday December 14th as it is being migrated to a new server.
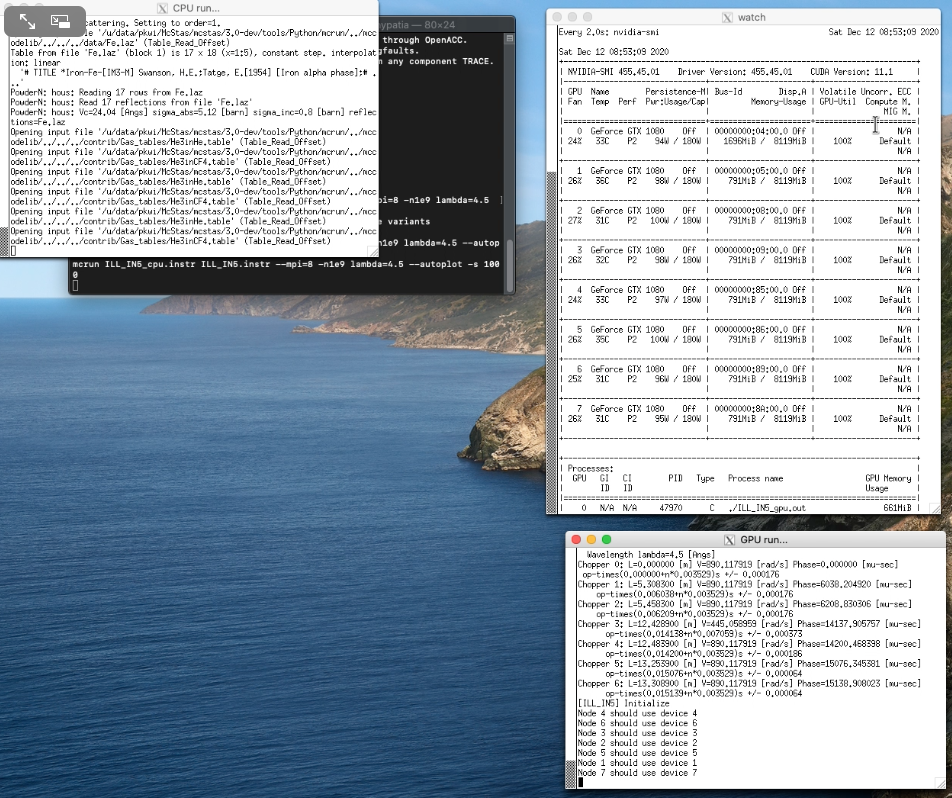
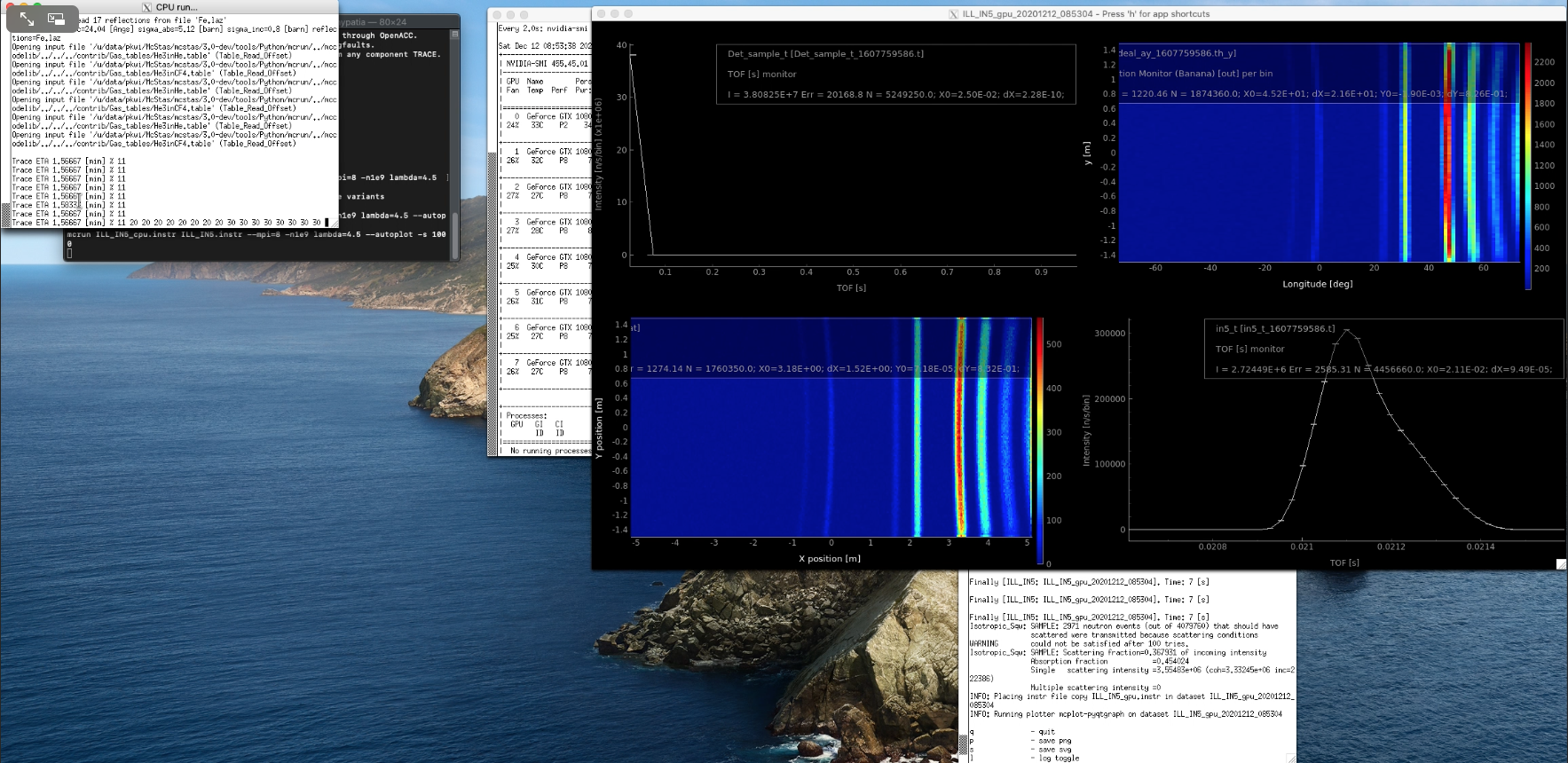
December 12th, 2020: Getting ready for McStas 3.0
We are closing in on the McStas 3.0 release, with support for NVIDIA GPU's using the nvc compiler and OpenACC.
To give you an idea of what to expect, here is a small demo video where an 1e9 run of ILL_IN5 is executed on 8 x NVIDIA GeForce 1080 and 8 x Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2687W:
Demo video (4:22 min, hosted at media.mcstas.org)
December 4th, 2020: NCrystal-package available on CentOS
Dear all,
The mcstas repo has been updated with an NCrystal-package which was missing in the CentOS package set from last Friday. To install it, please run:
yum install mcstas-ncrystal-2.7
As a bonus, the RPM package contains the newly released NCrystal 2.2.1 relase.
November 27th, 2020: McStas 2.7 release!
Dear all,
A new release of McStas, v. 2.7 has been built and is ready for download!
Download and installation instructions are available via our GitHub download pages.
Selected highligts from the release are listed below. The full list of changes is also available at http://mcstas.org/CHANGES_McStas.
(A small PS: Our build for CentOS will lack NCrystal for the time being, there are some issues compiling. Talks have been initiated with the NCrystal authors and the missing RPM is expected during next week.)
Changes in McStas v.2.7, November 27th, 2020
- McStas 2.7 is the 10th release in the 2.x series, provides minor incremental improvements and fixes various minor issues with McStas 2.6.1
- Thanks to all contributors of components, instruments etc.! This is what Open Source and McStas is all about!
- Installation:
- Our install docs are now available on the McCode GitHub pages
- Fixes of issues from last release:
- - A number of minor issues from 2.6.1 were addressed, see the relevant GitHub issues for details.
- Tools:
- On macOS (from 11.0 Big Sur onwards), mcgui will assume light/dark mode with the system settings. (The change came from using the system python3 with our app/miniconda-distributed Qt libs etc.)
- We now no longer officially support the perl/PGPLOT backend, these may or may not work on your system.
- Platforms:
- Nothing really new to report here. We still support 64bit Windows 10, all recent 64bit macOS including 11.0 Big Sur, Debian-based and RPM-based distros. (RPMs are built on/for CentOS, you may get varying milage elsewhere.)
- Libraries:
- Updated version 2.1.1 NCrystal library from T. Kittelmann (ESS) and X.X. Cai (CSNS), distributed with McStas on Unix
platforms only. To use it, carry out the below steps:
mcstas:~/NCryst$ mcstas-2.7-environment
mcstas:~/NCryst$ source $MCSTAS/ncrystal/setup.sh
mcstas:~/NCryst$ ncrystal_preparemcstasdir
mcstas:~/NCryst$ cp $MCSTAS/examples/NCrystal_example_mcstas.instr .
mcstas:~/NCryst$ mcrun -c NCrystal_example_mcstas.instr
- MCPL library from the same authors now included at v. 1.3.2.
- Updated version 2.1.1 NCrystal library from T. Kittelmann (ESS) and X.X. Cai (CSNS), distributed with McStas on Unix
platforms only. To use it, carry out the below steps:
- Components:
- Updated Union library from Mads Bertelsen, ESS DMSC.
- Cyl_monitor.comp, enriched with angular limits and dynamic allocation.
- Event_monitor_simple.comp, a simple ascii event-list monitor, good for debugging purposes
- Instruments:
- New "unit test" instruments for basic functionalities and key components:
- Random numbers and focusing
- Test_RNG_rand01.instr
- Test_RNG_randnorm.instr
- Test_RNG_randpm1.instr
- Test_RNG_randtriangle.instr
- Test_RNG_randvec_target_circle.instr
- Test_RNG_randvec_target_rect.instr
- Test_RNG_randvec_target_rect_angular.instr
- Monitors
- Sample components
- Test_Incoherent.instr
- Test_PowderN.instr
- Test_PowderN_concentric.instr
- Test_SX.instr
- Test_Sqw.instr
- Random numbers and focusing
- Various new instruments used for comparison with the forthcoming McStas 3.0 ILL_D2B_noenv.instr, ILL_H22_D1A_noenv.instr, ILL_H22_D1B_noenv.instr,
- Name change, TasResoTest.instr is now called Test_TasReso.instr
- Instruments providing earlier models of ESS moderators have been retired, i.e. are not in the release anymore: ESS_2001_bispectral.instr, ESS_2015_test.instr, ESS_Brilliance_2001.instr, ESS_Brilliance_2013.instr, ESS_Brilliance_2014.instr, ESS_Brilliance_2015.instr, ESS_Brilliance_TDR.instr
- New "unit test" instruments for basic functionalities and key components:
We hope you will enjoy this new release!!! (And keep an eye out for 3.0, it is almost also there...)
October 2nd, 2020: McStas presentation from the 2020 OpenACC summit now online
Dear all,
The McStas presentation from the OpenACC summit is now online on YouTube.
OpenACC (see https://www.openacc.org) is a high-level, compiler-driven approach to GPU-acceleration, and in the video McStas team tech-lead Peter Willendrup gives an overview about neutron scattering, McStas and how the team is porting the code to Nvidia GPU's.
Have a look at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HDU-WRJUZXs&feature=youtu.be
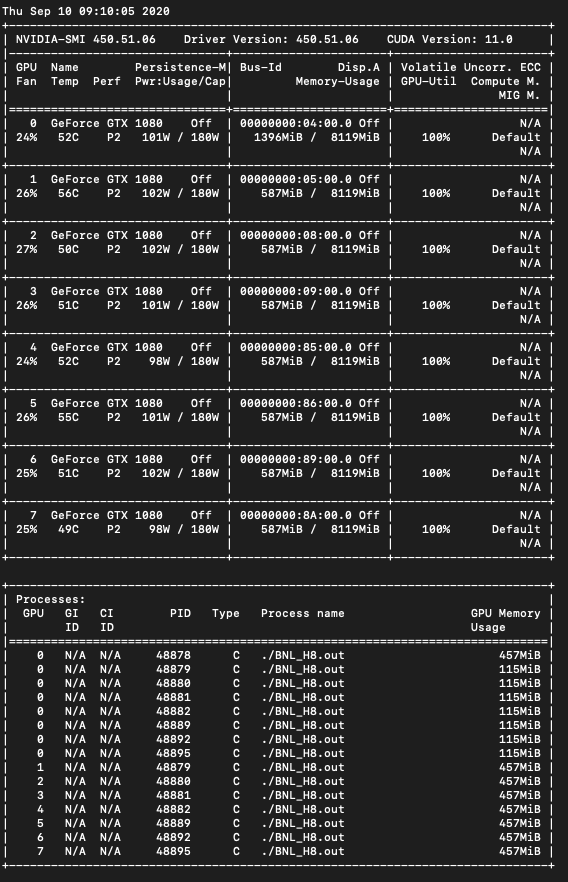
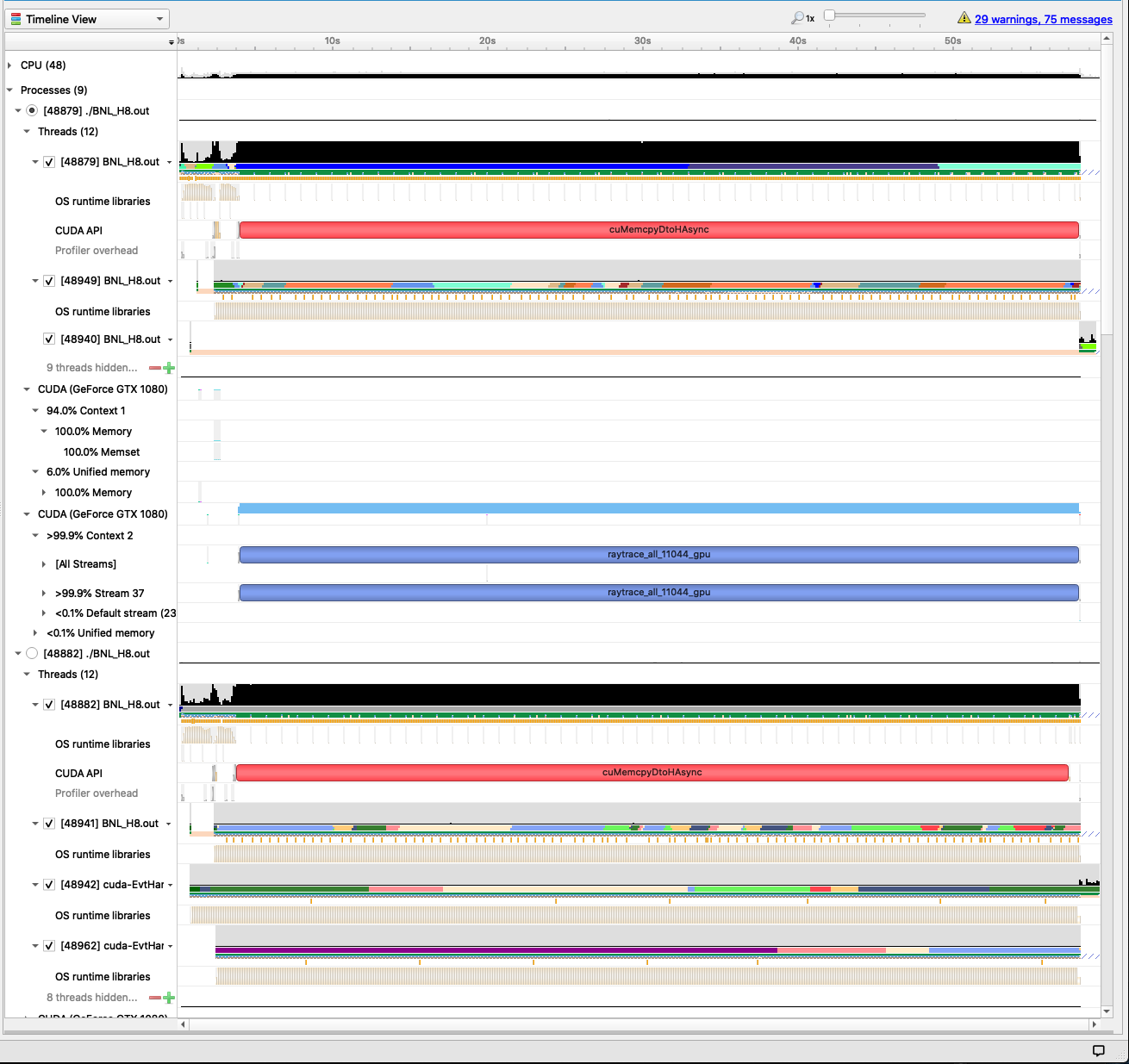
September 10th, 2020: Multi-GPU support in McStas 3 code tree
For Linux systems with multiple Nvidia GPU's the McStas team now has a solution, based on MPI and OpenACC. The images below show 8 NVIDIA GeForce 1080 running BNL_H8 in parallel and profiling-output in NVIDIA Nsight Systems:
The plan is to release either another beta or the first "real" McStas 3.0 before the end of 2020.
August 24th, 2020: macOS 11.0 Big Sur beta, hold your horses...
The McStas team has tested the current 2.6.1 release on the beta, and lots of stuff is broken on Big Sur...
We are aware that getting the freshest or forthcoming version of macOS can be tempting, but please wait for an updated McStas release if you aim to do any work with McStas... :-)
May 26th, 2020: Experimental McStas 2.6.1 and McXtrace 1.5 dockers
The combined McStas and McXtrace team have started experimenting with using Docker's for deployment. The advantage is simplified installation and a uniform look and feel / functionality across platforms.
If you feel like giving our experimental docker solutions a spin, have a look at https://github.com/mccode-dev/McCode/blob/master/Docker/README.md
May 4th, 2020: McStas 2.6.1 released
Dear all,
A new minor-release of McStas, v. 2.6.1 has been built and is ready for download!
Download and installation instructions are available via our GitHub download pages.
The release adresses a few bugs found in the 2.6 release, see the related issue list at GitHub, but is in terms of features and functionality almost identical to 2.6.
Best
Peter Willendrup
April 28th, 2020: McStas 2.6 on Ubuntu 20.04
Dear all,
I have tried out the McStas 2.6 release on the fresh Ubuntu 20.04 release, and my findings are these:
- Generally, the release works as expected - all of the python tools seem to function well.
- For the legacy perl tools we have the issue that the OS-provided
PDL no longer comes with a PGPLOT plotting-bridge, which affects
mcplot.pl and mcgui.pl:
mcstas@mcstas-virtual-machine:~$ mcgui.pl Can't locate PDL/Graphics/PGPLOT.pm in @INC (you may need to install the PDL::Graphics::PGPLOT module) (@INC contains: /usr/share/mcstas/2.6/tools/Perl/perl/modules /usr/share/mcstas/2.6/tools/Perl/perl /etc/perl /usr/local/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/perl/5.30.0 /usr/local/share/perl/5.30.0 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/perl5/5.30 /usr/share/perl5 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/perl/5.30 /usr/share/perl/5.30 /usr/local/lib/site_perl /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/perl-base) at /usr/share/mcstas/2.6/tools/Perl/perl/mcplotlib.pl line 23, line 207. BEGIN failed--compilation aborted at /usr/share/mcstas/2.6/tools/Perl/perl/mcplotlib.pl line 23, line 207. Compilation failed in require at /usr/bin/mcgui.pl line 2181, line 207.
- Of course the recommendation is to simply move to the Python
tools, but if you insist to stay with perl, please do a local
CPAN-based PDL installation like this:
sudo cpan install PDL
- Since a few releases, the default PGPLOT implementation on Ubuntu changed to Giza. Giza seems to now be getting better, see the April 30th 2018 hint if you want the legacy PGPLOT instead.
Best regards,
Peter Willendrup
February 27th, 2020: McStas 3.0beta bugfixes etc
- As we move along with the development on the mcstas-3.0 branch, you may find patched versions of components in the Updates folder found next to the distribution binaries at http://download.mcstas.org/mcstas-3.0beta/.
- A first bug with fix: Unfortunately, a buggy last-minute change to the PowderN component before mcstas-3.0beta was built introduced an error which makes it produce 0 scattered intensity. Please find an improved version in the above-mentioned Updates folder. Further bugfixes to this component are expected since the component produces scattering but has certain edge-case issues on GPU, especially at high ncount rates.
- At any time, know bugs will be listed as issues on GitHub marked with the label of "mcstas-3.0beta"
- Please do submit issues to GitHub as you find them: This will help in the process toward a stable, official 3.0 release!
February 25th, 2020: McStas 3.0beta technology preview available!
Dear all,
A technology preview for the forthcoming McStas 3.x series is now available for testing!
Main highlights of the release are:
- New code-generation scheme based on functions instead of #defines
- Much improved compilation-times, the code is better suited for modern compilers
- In most cases a speed-up of order 20% on CPU
- Limited, experimental support for OpenACC acceleration on NVIDIA GPU's
- Speedups measured using top-notch NVIDIA V100 datacenter cards are in the range of 10-600 with respect to a single-core CPU
- In essence, you will need a Linux machine with an NVIDIA card and the PGI compiler to make use of the GPU-support
For more details and instructions, please refer to this document on our Wiki
Thanks to:
- Thanks to all members of the joint McStas-McXtrace team, you guys ROCK!
- Thanks to Guido Juckeland (HZDR,DE) and Sebastian Alfthan (CSC,FI) who were behind the GPU Hackathons we participated in
- Thanks to our NVIDIA mentors Vishal Metha, Christian Hundt and Alexey Romanenko



January 24th, 2020: McStas 2.6 release!
Dear all,
A new release of McStas, v. 2.6 has been built and is ready for download!
Download and installation instructions are available via our GitHub download pages.
Selected highligts from the release are listed below. The full list of changes is also available at http://mcstas.org/CHANGES_McStas.
Changes in McStas v.2.6, January 24th, 2020
- McStas 2.6 is the eight release in the 2.x series and fixes various issues with McStas 2.5, plus new developments.
- Thanks to all contributors of components, instruments etc.! This is what Open Source and McStas is all about!
- Installation:
- Our install docs are now available on the McCode GitHub pages
- Fixes of issues from last release:
- A number of issues from 2.5 were corrected, see the relevant GitHub issues for details.
- Plus lots of work in general, see the relevant GitHub issues
- Tools
- Contribution from Tobias Weber ILL: Python-version of mcresplot.
- Libraries:
- Updated version 1.0.0 NCrystal library from T. Kittelmann (ESS) and X.X. Cai (CSNS), distributed with McStas on Unix platforms only. See the CHANGES document for full detail.
- MCPL library from the same authors now included at v. 1.3.0. See the CHANGES document for full detail.
- Updated version of the NXS lib from Mirko Boin HZB.
- Components:
- Updated Union library from Mads Bertelsen, ESS DMSC including
- New geometries, mesh (for stl file input in Union setups) and cone (e.g. relevant for describing anvils in pressure cells.
- New AF_HB_1D_process for modelling 1D antiferromagnetic Heisenberg chains and PhononSimple_process for modelling single-branchg acoustic phonons ala Phonon_simple
- New SINE2020-developed Union physics processes from Victor Laliena, Uni Zaragoza: Texture_process.comp and IncoherentPhonon_process.comp. See DOI:10.3233/JNR-190117.
- Shieldinglogger-components from Rodion Kolevatov, IFE for
estimating gamma-production in guides:
- Contributions Dose_calculator and Shielding_calculator
- Patched versions of optics-components: Elliptic_guide_gravity_shieldinglogger, Guide_channeled_shieldinglogger, Guide_curved_shieldinglogger, Guide_gravity_shieldinglogger, Guide_shieldinglogger
- Components patched / derived from the "scatterlogger" framework to model Ni and Ti layers seperately: Shielding_log_iterator_Ni_new, Shielding_log_iterator_Ti_new, Shielding_log_iterator_stop, Shielding_log_iterator_total, Shielding_logger.comp, Shielding_logger_stop.comp.
- See DOI:10.3233/JNR-190123, DOI:10.1016/j.nima.2018.12.069 and DOI:10.3233/JNR-180088.
- Please note that the included Shielding- and Dose- calculators will only give sensible for guides with borosilicate glass substrate. If the substrate is, e.g. copper, the dose rates from neutrons transmitted through the coating and captured in the substrate will overshoot the coating contribution significantly, so that shielding has to be enforced by few tens of centimeters of concrete.
- Guide_anyshape_r additions from Peter Link MLZ. Allows describing geometry in OFF format with reflectivity "per" face. Test instrument is Test_guides which has been updated to include this modified component.
- Vertical_Bender from Andrew Jackson ESS and Richard Heenan STFC. Allows modelling a multi-channel bender that curves vertically down.
- SANS_spheres2 by Peter Willendrup, derived from Henrich Frilinghaus' SANS_benchmark2. More realistic cross-section calculations than from e.g. Sans_spheres. templateSANS2.instr is the related test instrument.
- Updated version of Sample_nxs from Mirko Boin HZB.
- Single_magnetic_crystal.comp is an experimental magnetic csingle crystal model. Its operational model is based on that of Single_crystal.comp but supports SF and NSF magnetic scattering. The present model only supports the SF-NSF paradigm along a given reference vector.
- PSD_monitor_4PI_spin.comp is a version of PSD_monitor_4PI but with separate SF- and NSF-channels
- Updated Union library from Mads Bertelsen, ESS DMSC including
- Instruments:
- Union_test_texture.instr demonstrates use of Texture_process.comp by Victor Laliena. To be used with datafile "coef_Four_L2.txt" found in the installation data-folder. This datafile contains texture information on Zr alloys derived from DOI:10.1016/j.jnucmat.2018.08.003.
- Union_IncoherentPhonon_test.instr demonstrates use of IncoherentPhonon_process.comp by Victor Laliena. To be used with datafile "dos_meV.txt" found in the installation data-folder.
- Union_test_mesh.instr demonstrates use of mesh geometry in Union
- ESS_BIFROST_shielding.instr and PSI_Focus_shielding.instr, demonstration of Shielding_logger concept from Rodion Kolevatov
- TasResoTest, triple-axis resolution test instrument from Tobias Weber ILL. Can be used with his new tool development mcresplot.py.
- Tools_ONION, instrument to investigate q-resolution via Mantid, by Thomas Huegle, ORNL. See also DOI:10.1016/j.nima.2019.162711 and the related python code available at our new "snippet" repository that should eventually replace the old "share" part of this webpage.
- templateSANS_MCPL, behaves like the normal templateSANS but dumps all events in an MCPL file.
- MCPL-oriented tool-instruments by Peter Willendrup. See the CHANGES document for full detail.
- SINE2020-developed McStas_Isotropic_Sqw, McStas_PowderN, McStas_Single_crystal by Erik Knudsen. They have MCPL input/output and are intended for easy use of McStas samples within SIMRES.
- Test_guides has been modified to include Guide_anyshape_r from Peter Link MLZ.
- templateSANS2 serves as test instrument for SANS_spheres2.
- Test_single_magnetic_crystal.instr is a skeleton Laue camera which exemplfies use of Single_magnetic_crystal.comp
- Datafiles:
- Klaus Lieutenant from FZJ/Vitess has collected reflectitivy-data from SwissNeutronics, Mirrotron and S-DH, analysed
these and fitted the "classical" McStas mirror-reflectivity profile to these. The resulting data have been placed
in the data directory under the filenames of
- SwissNeutronics_mirors_2020.txt
- Mirrotron_mirors_2020.txt
- S-DH_mirors_2020.txt.
- The files are not to be used directly with reflecting components, but can instead be used as lookup-tables for relevant parameters in each case. I.e. for a mirror of nominal m-value m_nom, use m_real, R_0, W and alpha from the relevant table.
- Klaus Lieutenant from FZJ/Vitess has collected reflectitivy-data from SwissNeutronics, Mirrotron and S-DH, analysed
these and fitted the "classical" McStas mirror-reflectivity profile to these. The resulting data have been placed
in the data directory under the filenames of
We hope you will enjoy this new release!!!
Previous news items: 2019, 2018, 2017, 2016, 2015, 2014, 2013, 2012, 2011, 2010, 2009, 2008, 2007, 2006, 2005, 2004, 2003, 2002, 2001, 2000, 1999, 1998.